Group No.10 Others
① Anodizing (anodic oxide coating)
■What is anodizing (anodic oxide coating)?
Anodizing (anodic oxide coating) is a surface treatment using anodizing processing to give decorativeness, durability, and corrosion resistance to aluminum surfaces.
■Main features
The anodizing (anodic oxide coating) improves corrosion resistance, surface hardness and surface insulating property.
The anodic oxide coating film can be died. Depending of material of parts, the coating gives a decorative value.
*Full function:DRILUBE (THAILAND) CO.,LTD

Application example of anodizing (anodic oxide coating)

Sectional view of anodic oxide coating film
② Black oxide coating (black finishing)
■What is a black oxide coating?
A black oxide coating is a surface treatment that improves corrosion resistance. By immersing a metal part, such as an iron part, in a high-temperature treatment fluid, a fine-grained black oxide coating is formed on the surfaces.
■Main features
The black oxide coating improves the corrosion resistance and aesthetic appearance (it depends on material) of parts.
Photographs of the appearance of
the Black Oxide coating

Application example of black oxide coating
③ Manganese phosphate treatment
■What is a manganese phosphate treatment?
A manganese phosphate treatment is a chemical conversion treatment to create a manganese-phosphate-based crystalline film on the surfaces of ferrous material chemically.
■Main features
By creating an insoluble manganese phosphate film on the surfaces of ferrous material, the corrosion of the surfaces can be retarded. The treatment can be also used as an undercoat for ferrous material before painting.
Photomacrographs of the appearance of the
Manganese phosphate

Photographs of the appearance of the
Manganese phosphate
④ Calcium zinc phosphate treatment
■What is a calcium zinc phosphate treatment?
A calcium zinc phosphate treatment is a chemical conversion treatment to create a calcium-zinc-phosphate-based crystalline film on the surfaces of ferrous material chemically.
■Main features
By creating an insoluble calcium zinc phosphate film on the surfaces of ferrous material, the corrosion of the surfaces can be retarded. The treatment can be also used as an undercoat for ferrous material before painting.

Photomacrographs of the appearance
of the Calcium zinc phosphate

Photographs of the appearance of the
Calcium zinc phosphate
⑤ Salt-bath nitrocarburizing treatment
■What is salt-bath nitrocarburizing?
Salt-bath nitrocarburizing is a chemical conversion treatment to create a nitride layer on the surface of a base material using a salt bath that contains nitrogen and carbon.
■Main features
A nitrocarburized layer has the following features: wear resistance, anti-seizing property, heat resistance, and corrosion resistance.
Compared to other heat treatments, the treatment temperature of salt-bath nitrocarburizing is relatively low (approximately 500-600℃). Therefore, deformation caused by the heat treatment can be curbed.
**Material:Fe
*Full function:ZHONGSHAN CITY SUN-MIN METAL TREATMENT CO., LTD.
KUNSHAN SUNMIN - DRILUBE ELECTRONIC MATERIAL TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD.
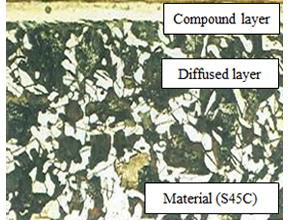
Sectional view of Salt-bath nitrocarburizing
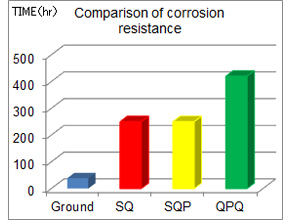
The comarison result of corrosion resistance
(Salt spray test material:C45)
⑥ Carbonitriding
■What is carbonitriding?
Carbonitriding is a heat treatment to improve wear and corrosion resistance of the surfaces of material by permeating a small amount of nitrogen into a carburized layer.
■Main features
Features of a carburized layer: To improve fatigue resistance, wear resistance, elastic limit, etc.
Since the treatment temperature of carbonitriding is low, deformation of material can be curbed.
**Material:Fe
*Full function:ZHONGSHAN CITY SUN-MIN METAL TREATMENT CO., LTD.
KUNSHAN SUNMIN - DRILUBE ELECTRONIC MATERIAL TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD.
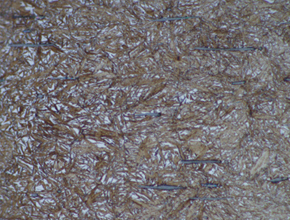
Photomacrographs of the
appearance of the Carbonitriding

Photographs of the appearance of the
Carbonitriding
⑦ Magnetic annealing
■What is magnetic annealing?
Magnetic annealing is a heat treatment to increase a crystal grain size of ferromagnetic material and reduce the magnetic flux density and magnetism retentivity.
■Main features
Features of magnetic annealing: To improve a magnetic property, magnetic flux density, etc.
Magnetic annealing is mainly used for soft magnetic iron cores.
*Material:Fe(pure iron)
*Full function:ZHONGSHAN CITY SUN-MIN METAL TREATMENT CO., LTD.
KUNSHAN SUNMIN - DRILUBE ELECTRONIC MATERIAL TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD.

Before Magnetic annealing (×1000)

After Magnetic annealing (×1000)
⑧ Quenching and Tempering
■What is quenching?
Quenching is a heat treatment to harden metallic material and improve wear resistance, tensile strength, and fatigue strength by cooling the material rapidly from high temperatures.
■Main features
(Quenching) Rising of hardness/ Rising of abrasion resistance and tensile strength ,fatigue strength etc.
■What is tempering?
Tempering is a heat treatment to reduce residual stress in metallic material and give ductility to the metal structure by reheating the material after quenching.
■Main features
(Tempering) Stabilization of metal structure / Reduction of residual stress / Rising of toughness etc.
*Material:Fe
*Full function:ZHONGSHAN CITY SUN-MIN METAL TREATMENT CO., LTD.
KUNSHAN SUNMIN - DRILUBE ELECTRONIC MATERIAL TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD.
* Selection conditions may change depending on your applications and material to be used. For more information, please contact us.
* The data shown above are for your reference only. The numerical values described on this page are not guaranteed.

Photomacrographs of the appearance
of the Quenching and Tempering

Application examples of quenching and tempering
⑨ Assembling / Mounting
■What is the assembly?
We offer not only decorating the interior/exterior parts made of metal, resin (plastic), rubber, etc. and home appliance parts, but also offer a consistent service that includes the assembly/mounting of those into a unit for meeting the customer needs for delivery.
■Features of Assembling/Attaching
We also offer the adhesives for attaching to the interior/exterior parts, and the application of a quick-drying lubricant, LUBICK, etc. as a preventive measure against the rubbing noise when sliding.

Attaching a Connector

Attaching Non-Woven Fabric
⑩ Laser marking
■What is laser marking?
Laser marking is a process that causes the partial imprinting or peeling by irradiating a laser beam on the substrate to be processed.
■Features of the laser marking process
A partial peeling off or engraving using a laser may be applied to the coated film.
When applying the laser marking to a black film, the coloration may be enhanced by inserting the color white into the undercoat.

Laser marking on black film without base coating

Laser marking on black film with base coating
using a white film for improved coloration